Hello, esteemed mycophiles and curious minds alike! Whether you’re a seasoned mycologist or a fledgling fungus fanatic, we’ve got a treat for you. Prepare to dive into the fascinating world of fungi, where science meets wonder. So, grab your magnifying glass, and let’s embark on a spore-filled adventure!
SCIENTIFIC NAME:
(Imleria Badia)
COMMON NAME(S):
Bay Bolete | Chestnut Bolete | Curiosity Cap | Woodland Wonder
I-NAME:
BAYB
Founding Mycologist/Discovered By:
Originally described by Elias Magnus Fries, the renowned Swedish mycologist, Imleria Badia was later reclassified, but the legacy of Fries’ discovery still enriches our mycological databases!

SPORE COLOR:
BROWN
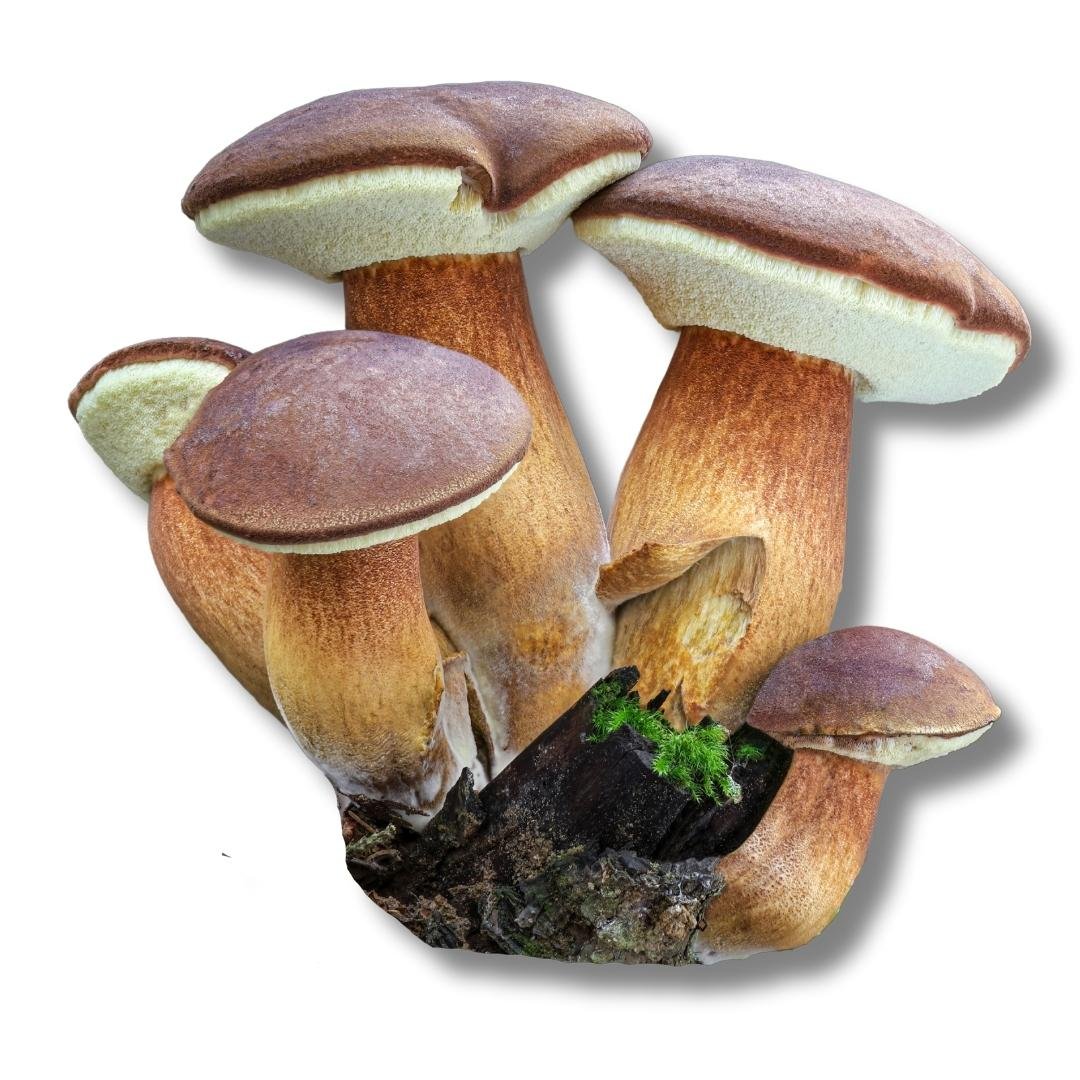
Whispered about in the dense woods, the Bay Bolete is a true woodland treasure. Its rich, chestnut cap and stout stature make it a distinguished presence amidst the leaf litter. Come along as we unearth the secrets of Imleria Badia, a mushroom as delectable as it is beautiful.
DESCRIPTION:
Sporting a smooth, bay-brown cap that spans 5-15 cm, the Bay Bolete stands proud with its robust stem. Its surface is dotted with a network of fine pores, exuding an earthy aroma that whispers tales of the forest. This mushroom isn’t just a feast for the eyes but has graced many historical plates with its nutty flavor.
INTENDED USES:


HISTORICAL & CULTURAL INFO:
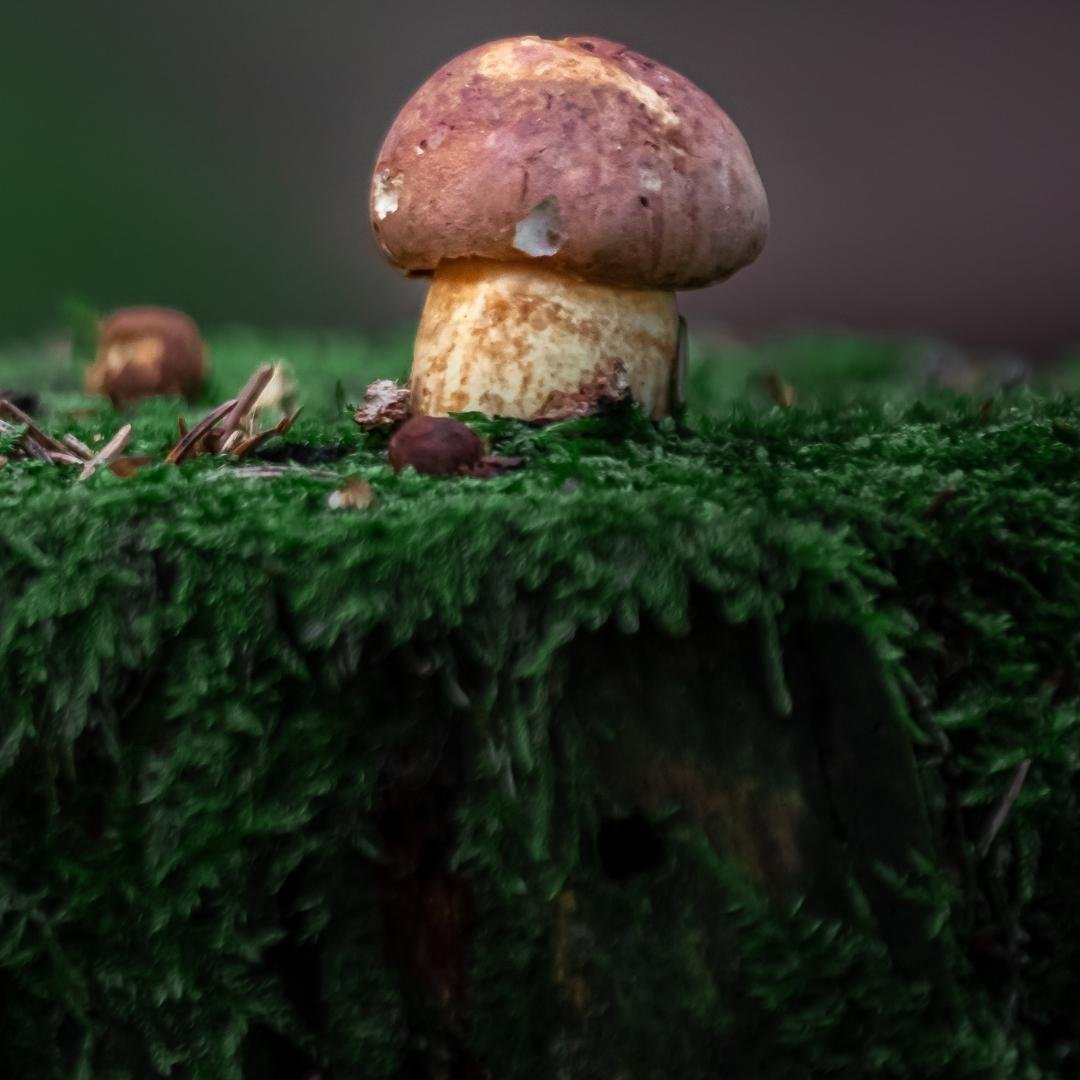
Imleria Badia is part of the Boletaceae family, cousins to the famed porcini. Its lineage is rooted deep in the woodlands of the Northern Hemisphere, with a history intertwined with European culinary traditions.
GENETIC LINEAGE/HISTORY:
In European folklore, the Bay Bolete is more than a mushroom; it’s a symbol of the forest’s generosity. It has graced tables for centuries, featuring in folklore and cuisines, and remains a cherished find for foragers.
CHEMICAL COMPOSITION:
Nutritionally, Imleria Badia is rich in vitamins and minerals. Its chemical makeup is a cornucopia of compounds that have nourished humans and animals alike through the ages.
HEALTH BENEFITS (if applicable):
While not hailed as medicinal, the Bay Bolete’s nutritional profile makes it a healthy addition to any diet. Its fibers and vitamins support a balanced, nature-inspired lifestyle.
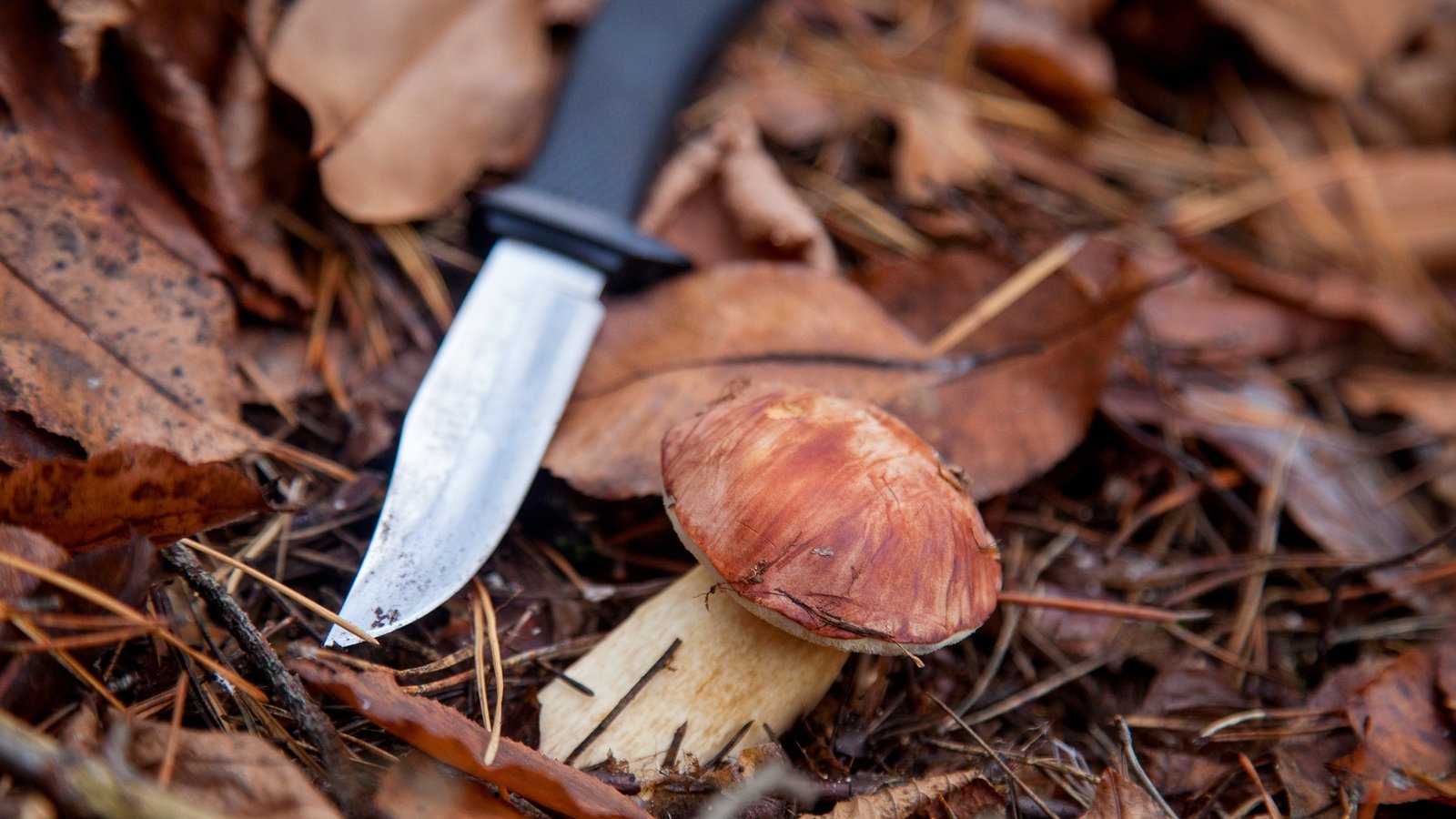

CAUTIONS & WARNINGS:
Always ensure correct identification before consumption. While Imleria Badia is a safe and edible mushroom, it has look-alikes that may not be as forgiving. When in doubt, consult an expert.
It is important to consult a doctor before consuming any mushrooms, especially if you have a pre-existing medical condition or are taking medication.
FINAL CONSIDERATIONS:
The Bay Bolete is a testament to nature’s bounty. Don’t miss the chance to explore the rich tapestry of its history and flavors. Visit our 🍄 Marketplace, where the world of fungi awaits at your fingertips.
Don’t let this fungal delight slip through your fingers! Our stock of Bay Bolete products moves as swiftly as the autumn winds. Secure your piece of the forest today!
Don’t forget to check out the 🍄 Mushroom Network’s Marketplace to see what’s available. But hurry, our shelves are constantly evolving, and you wouldn’t want to miss out on this wonderful mushroom. Join our growing network of Patrons, Genetics, and Mycologist Vendors only on the 🍄 Mushroom Network!
While typically wild-foraged, there have been successful attempts at cultivating Imleria Badia, making it a fascinating prospect for aspiring mycologists.
Absolutely! Its distinctive features make it a great introductory mushroom for budding foragers.
Imleria Badia can be distinguished by its bay-brown cap, yellow-brown to olive pores that turn blue when bruised, and a net-like pattern on its stem. Always cross-check with a field guide or consult an expert for accurate identification.
The Bay Bolete is predominantly found in European woodlands, particularly under conifers and broad-leaved trees. It thrives in a symbiotic relationship with the roots of living trees.
Imleria Badia typically fruits from late summer to late autumn. The peak season may vary depending on regional climate and weather patterns.
Freshly foraged Bay Boletes should be stored in a breathable container like a paper bag or basket and kept in a cool place. For longer storage, they can be dried, frozen, or pickled.
While Imleria Badia is generally easy to identify, it’s important to be cautious as there are toxic species with some resemblance. Always forage with a knowledgeable guide or consult reliable resources.
Sustainable foraging practices are crucial. Avoid over-harvesting and damaging the mycelium to ensure the continued health and abundance of Imleria Badia populations.
While typically found in the wild, there have been successful attempts to cultivate Imleria Badia using mycorrhizal inoculation techniques. However, it remains a challenging species to cultivate for most hobbyists.
The Bay Bolete is a versatile mushroom in the kitchen, excellent in stews, soups, sautéed dishes, and as a meat substitute. Its nutty flavor enriches any recipe calling for mushrooms.
Related Articles:
Bay Bolete (Imleria Badia)
Hello, esteemed mycophiles and curious minds alike! Whether you’re a seasoned mycologist or a fledgling...
Read More...Other Mushroom Species To Research:
Hen of the Woods (Grifola Frondosa)
Scientific Name: Grifola Frondosa COMMON NAME(S): Hen of the Woods | Maitake The Hen of...
Read More...Bitter Oyster (Panellus Stipticus)
Welcome, esteemed mycologists and curious minds! Today, we delve into the intriguing world of Panellus...
Read More...Bleeding Fairy Helmet (Mycena Haematopus)
Greetings, fungal aficionados and curious minds! Today, we delve into the enigmatic world of Mycena...
Read More...Violet Webcap (Cortinarius Violaceus)
Welcome to the detailed exploration of Cortinarius Violaceus, a mushroom as intriguing as it is...
Read More...Other Recommended Reads:
The Art of Taxonomy: Understanding Mushroom Classification
Welcome to the captivating world of mycology, where the smallest spore can open a universe...
Read More...Rye TEK for Mycology: A Comprehensive Guide
Discover the magic of Rye grains, an esteemed substrate within the world of mycology. Often...
Read More...Mushroom’s Metropolis: Designing Fungi-Inspired Future Cities
The incredible design of the mycelial network has inspired scientists, architects, and city planners. From...
Read More...The Psilocybin Pioneer: Unearthing the History and Impact of Maria Sabina
In the study of mycology, Maria Sabina emerges as a legendary figure. A Mazatec curandera,...
Read More...