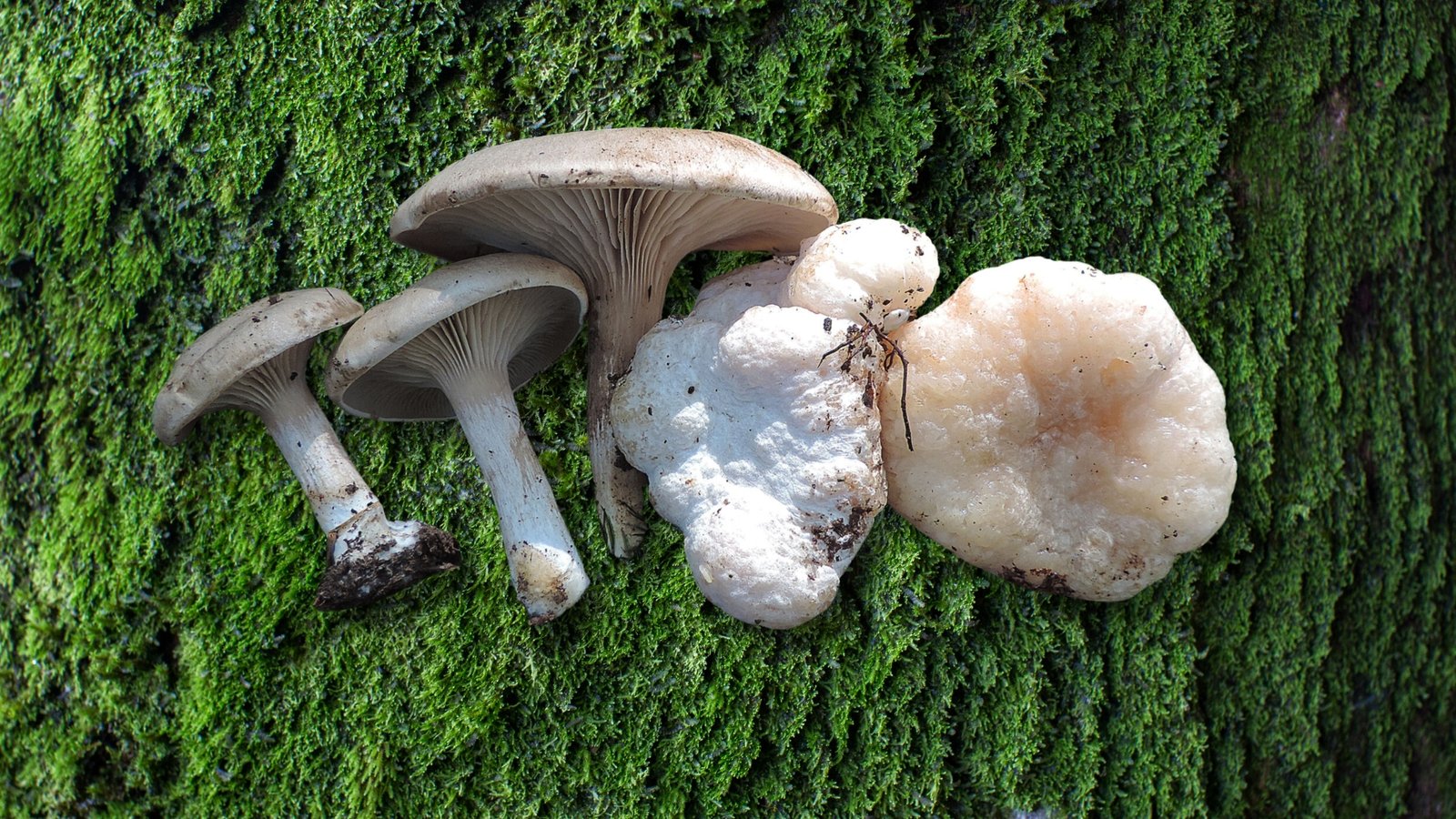
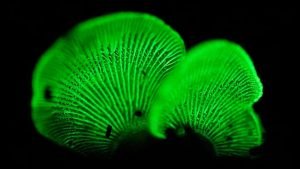
Welcome, mycophiles and curious minds, to a fascinating exploration of the Entoloma Abortivum – a mushroom that’s as intriguing as its name suggests! Get ready for a journey through the woods of wonder, where science and a touch of whimsy intertwine.
SCIENTIFIC NAME:
(Entoloma Abortivum)
COMMON NAME(S):
Aborted Entoloma | Shrimp of the Woods | Abortive Entoloma
I-NAME:
SHMP
Founding Mycologist/Discovered By:
-Unknown-
If you have information, please help us enrich our database!

RECOMMENDED TEMPERATURES
Colonizing Temps:70° – 75° | Fruiting Temps:65° – 70° |
SPORE COLOR:
PALE-PINK to BUFF
Meet the Aborted Entoloma, a mushroom that’s as mysterious in origin as it is unique in appearance. Often mistaken for something out of a fairy tale, this fungus plays a fascinating role in forest ecosystems and has piqued the interest of mycologists worldwide.
DESCRIPTION:
The Shrimp of the Woods is known for its irregular, bulbous structures resembling small, misshapen puffballs. They have a whitish to tan color and a firm, somewhat rubbery texture. Their appearance often sparks curiosity and wonder, making them a standout in the fungal kingdom.
INTENDED USES:

🔬 Mycological Study – A subject of ecological and biological research due to its unique growth and interaction with other species.
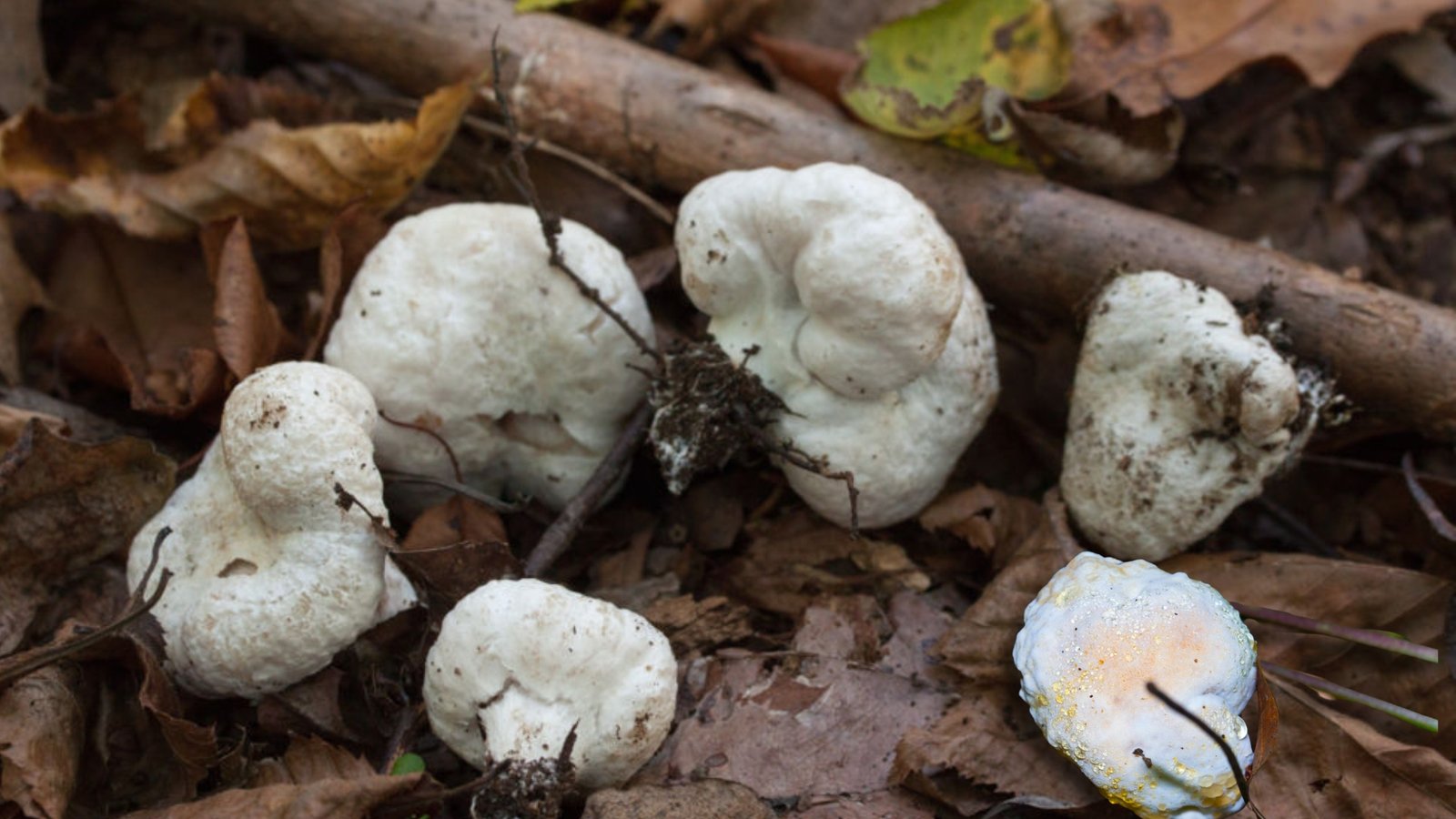

HABITAT AND DISTRIBUTION:
Naturally found in deciduous forests, often near hardwood stumps. It thrives in moist, shaded environments and is widely distributed across North America.
ECOLOGICAL ROLE:
This mushroom has a unique ecological role, often found in association with Honey Fungus (Armillaria spp.), indicating a complex ecological interaction.
GROWTH AND CULTIVATION:
While not commonly cultivated, the Aborted Entoloma grows readily in its natural habitat. Cultivation remains a challenge, requiring a deep understanding of its symbiotic relationships.
No posts found!
HISTORICAL & CULTURAL INFO:
The Shrimp of the Woods has long fascinated mycologists and foragers. Its unique appearance and edibility have made it a subject of folklore and culinary experimentation, adding to the rich tapestry of mushroom lore.
GENETIC LINEAGE/HISTORY:
Research into its genetic lineage is ongoing, with recent studies shedding light on its relationship with other fungi, particularly Armillaria.
No posts found!
CHEMICAL COMPOSITION:
Contains various nutrients typical of edible mushrooms. Its chemical makeup is a subject of ongoing research, particularly regarding its interaction with other fungi.
MEDICINAL PROPERTIES (if applicable):
Currently, there are no widely recognized medicinal properties. However, its nutritional value as an edible mushroom is notable.
CULINARY USES (if applicable):
Appreciated for its unique texture and flavor, the Shrimp of the Woods is a delicacy in gourmet cooking. It can be sautéed, grilled, or used in soups, often as a meat substitute or seafood alternative.
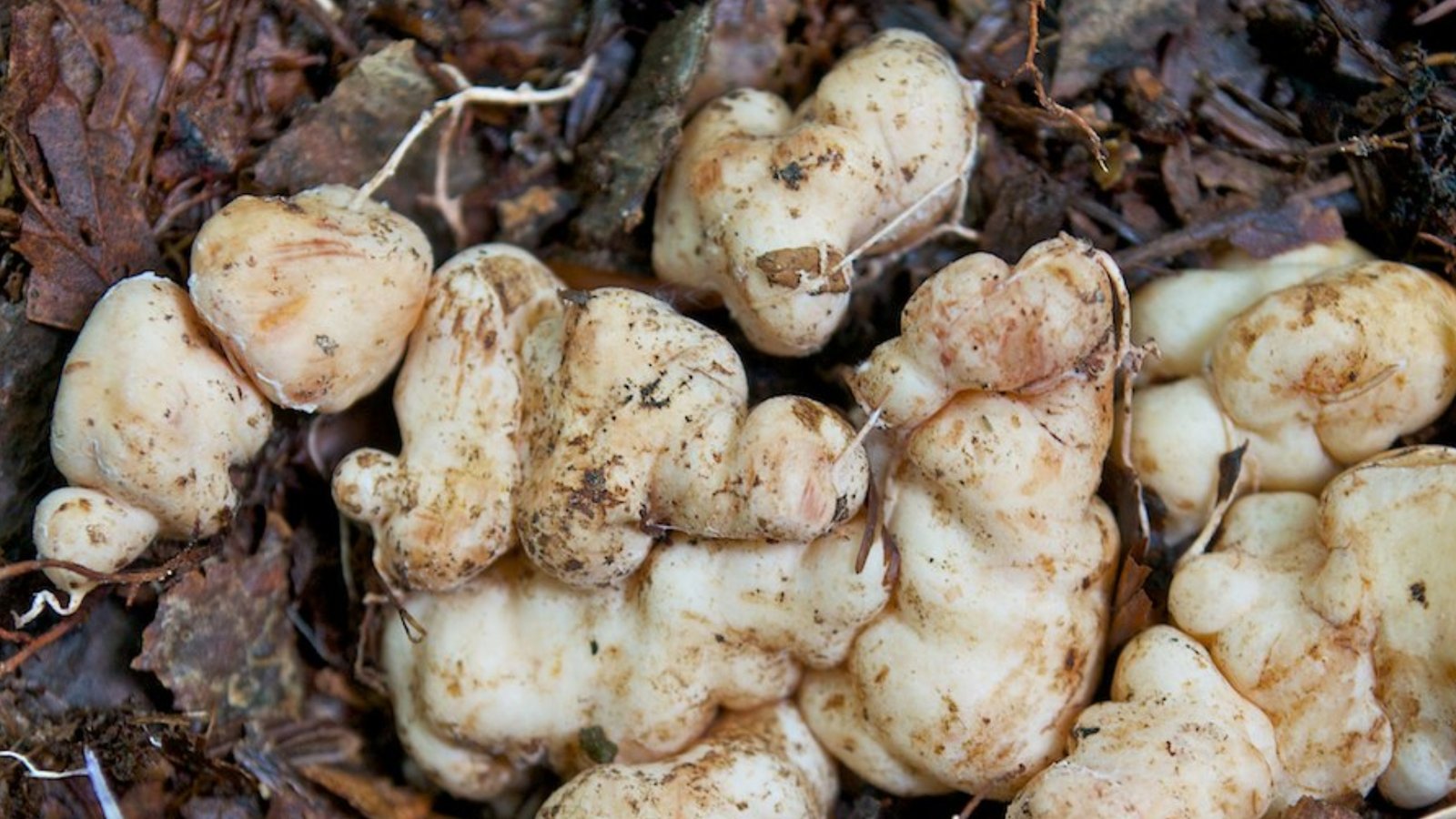

CAUTIONS & WARNINGS:
While edible, it’s crucial to accurately identify this mushroom, as it can be confused with toxic varieties. It is important to consult a doctor before consuming any mushrooms, especially if you have a pre-existing medical condition or are taking medication.
FINAL CONSIDERATIONS:
The Aborted Entoloma remains a mysterious yet captivating character in the world of fungi. Don’t miss the chance to explore this enigmatic mushroom in our 🍄 Marketplace, where the wonders of mycology are just a click away.
Don’t forget to check out the 🍄 Mushroom Network’s Marketplace to see what’s available. But hurry, our shelves are constantly evolving, and you wouldn’t want to miss out on this wonderful mushroom. Join our growing network of Patrons, Genetics, and Mycologist Vendors only on the 🍄 Mushroom Network!
No posts found!
No posts found!
FAQs:
Yes, when correctly identified and properly prepared.
It has a mild, somewhat nutty flavor with a firm texture.
Home cultivation is challenging due to its complex ecological relationships.
Typically in deciduous forests, near hardwood stumps.
Look for its unique, bulbous, and irregular shape, but always seek expert verification.
Related Articles:
Shrimp of the Woods (Entoloma Abortivum)
Welcome, mycophiles and curious minds, to a fascinating exploration of the Entoloma Abortivum – a...
Read More...Other Mushroom Species To Research:
Violet Webcap (Cortinarius Violaceus)
Welcome to the detailed exploration of Cortinarius Violaceus, a mushroom as intriguing as it is...
Read More...Bay Bolete (Imleria Badia)
Hello, esteemed mycophiles and curious minds alike! Whether you’re a seasoned mycologist or a fledgling...
Read More...Shiitake (Lentinula Edodes)
Welcome to another fascinating journey through the mycological marvels of our planet. Today, we’re diving...
Read More...Bitter Oyster (Panellus Stipticus)
Welcome, esteemed mycologists and curious minds! Today, we delve into the intriguing world of Panellus...
Read More...Other Recommended Reads:
The Health Benefits of White Oyster Mushrooms
White Oyster Mushrooms (Pleurotus Ostreatus) are prized globally not just for their culinary versatility but...
Read More...Protected: ##################
There is no excerpt because this is a protected post.
Read More...Pale Brittlestem (Psathyrella Candolleana)
Scientific Name: Psathyrella Candolleana COMMON NAME(S): Pale Brittlestem | Candolle’s Brittlesteam Psathyrella Candolleana is a...
Read More...Fungi Flatulence and Other Mycological Marvels That’ll Make You Go “Whaaat?”
About This Article: This is where you can leave notes or details that only ADMINS...
Read More...Whoa there, Spore Sport! 🍄 Looks like you’re not logged in yet. Don’t you know what you’re missing? MYCO-CREDITS! Imagine all the fungal fun you could have. It’s like finding a Morel in May and not picking it. Tragic, right? Log In or Become a Myco-Patron and start racking up those credits. It’s more rewarding than finding a mushroom in your backyard! 🌟🏡