Cordyceps Militaris: The Caterpillar Fungus embarks on a journey to unravel the unusual life cycle, ecology, and unique features of Cordyceps, a fascinating fungal genus. This enthralling exploration ventures into the worlds of entomology and mycology, bringing to light the captivating symbiosis that births this remarkable fungus.
Cordyceps Militaris: A Peculiar Parasite:
Cordyceps is a genus of ascomycete fungi that comprises over 400 species, but the one that has captured the most attention is Cordyceps Militaris. Known as the caterpillar fungus, this species is famous not just for its bright orange fruiting body but also its rather peculiar life cycle that involves a rather dark but fascinating relationship with insects.
The caterpillar fungus owes its name to its unusual parasitic relationship with insect hosts. Instead of decomposing organic matter like many other fungi, Cordyceps Militaris has adapted to parasitize various species of insects and arachnids, most notably the pupae of Lepidoptera, the order that includes butterflies and moths.
The story of this bizarre relationship starts when a Cordyceps Militaris spore lands on a suitable host. The spore germinates, and the resulting mycelium invades and eventually consumes the host’s body from the inside, absorbing nutrients and growing. When the time comes for the fungus to reproduce, it forms a fruiting body that erupts from the host’s carcass, releasing a new generation of spores into the environment.

The Life Cycle of Cordyceps Militaris:
The life cycle of Cordyceps Militaris is a fascinating demonstration of nature’s complex interplay. The first stage of the life cycle begins when airborne spores of the fungus land on a host insect. These spores attach to the insect’s outer shell and germinate, forming thread-like hyphae that penetrate the host’s body.
Inside the host, the fungus continues to grow, feeding off the insect’s nutrients. It eventually takes over the host’s body, leaving the insect alive but under the fungus’s control. This parasitic relationship is a remarkable instance of a phenomenon known as host manipulation, where parasites alter the behavior of their hosts to increase their own survival and reproduction.
Finally, the host insect dies, and the fungus begins to produce a fruiting body, or stroma. This stroma emerges from the insect’s body, growing upward into a long, club-like structure. This structure eventually produces and releases a new generation of spores, completing the life cycle and perpetuating the fascinating, if somewhat gruesome, existence of this unusual fungus.
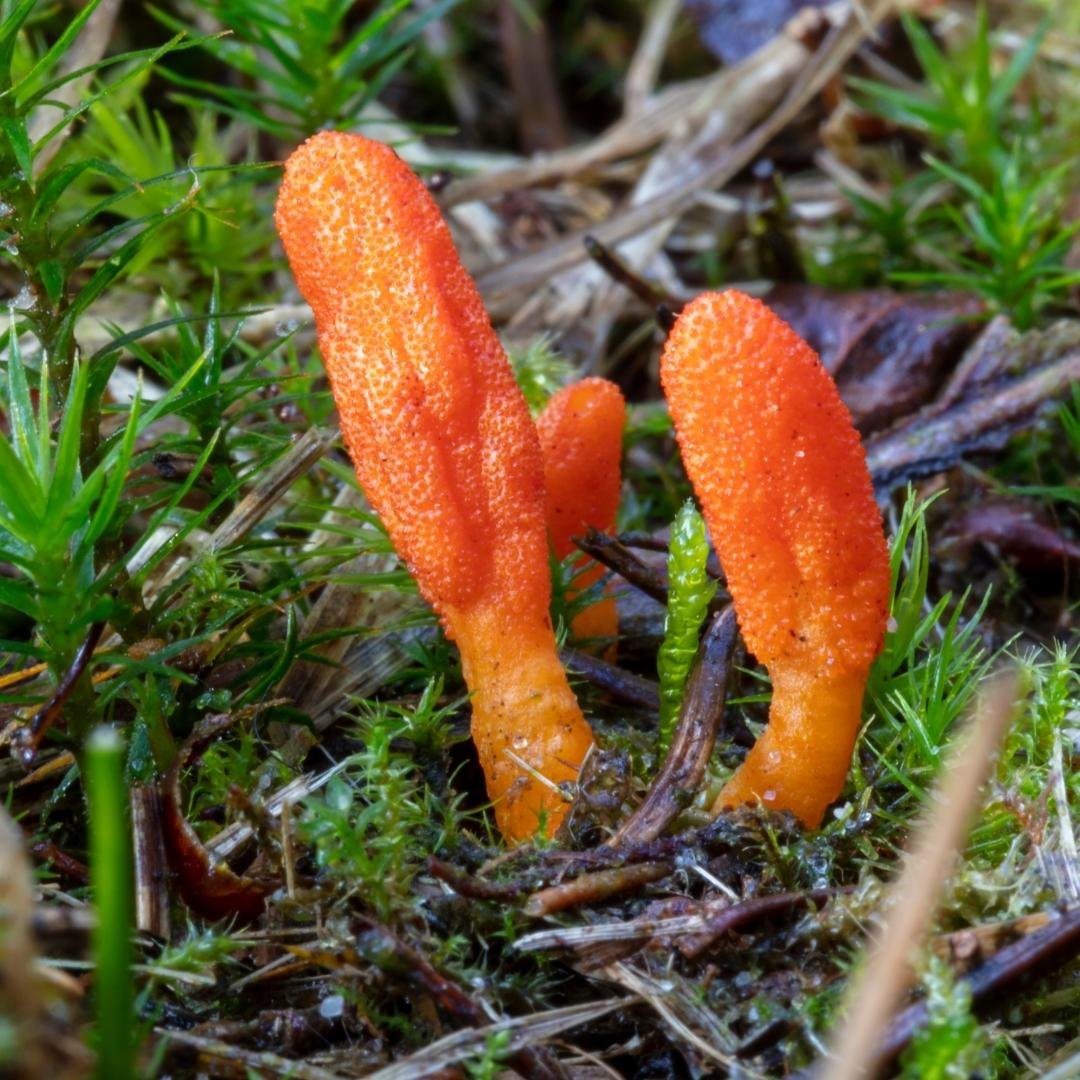

Ecology and Distribution:
Cordyceps Militaris is found worldwide, occurring predominantly in North America, Europe, and Asia. It prefers temperate habitats and is typically found in forested areas, meadows, and places with an abundance of potential insect hosts.
This fungus shows a preference for certain types of insects, particularly the pupae of Lepidoptera (butterflies and moths), but can also parasitize other insects and arachnids. Because of its unique lifestyle, Cordyceps Militaris plays a unique role in its ecosystem. It helps control insect populations, thus contributing to the ecological balance.
Despite its gruesome lifestyle, Cordyceps Militaris is also an important part of the food chain. Various small mammals and insects feed on the fruiting bodies of the fungus, while the spores serve as food for numerous microscopic organisms.
The universe of mushrooms is expansive, each variant bearing its own unique charm and characteristics. The Marketplace on the 🍄 Mushroom Network is a testament to this diversity. It is a haven for those seeking a deeper understanding of the magical world of mushrooms. If you’re keen on learning more about this type of mushroom and other mushroom variants, this Marketplace is your ultimate resource.
No posts found!
Unique Features and Human Uses:
Beyond its unusual life cycle and ecological role, Cordyceps Militaris holds a unique place in human culture and medicine. For centuries, various species of Cordyceps have been used in traditional medicine, especially in Asia. Cordyceps Militaris, in particular, is valued for its potential health benefits.
This fungus contains several bioactive compounds, including cordycepin and polysaccharides, which have been studied for their potential antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, and anti-cancer effects. Moreover, Cordyceps Militaris has been researched for its potential to boost physical performance, leading to its use as a supplement among athletes.
Interestingly, Cordyceps Militaris also has culinary applications. Its fruiting bodies have a unique flavor that has been described as slightly sweet and nutty, making it a sought-after ingredient in certain gourmet dishes.
Not sure where to start? The 🍄 Mushroom Academy offers a wide range of courses tailored to your needs. Whether you’re a beginner eager to learn or an experienced mycologist looking to broaden your knowledge, the 🍄 Academy has something for everyone.

Fungal Fascination: Preparing for the Conclusion:
As we traverse the final stage of our exploration, we are left in awe of the peculiar life of Cordyceps Militaris. A parasitic puppeteer, an ecological balancer, a potential medicinal powerhouse, and a culinary delight, this fungus truly is a testament to the boundless fascination that the kingdom of fungi holds.
Don’t forget to check out the 🍄 Mushroom Network’s Marketplace to see what’s available. But hurry, our shelves are constantly evolving, and you wouldn’t want to miss out on this wonderful mushroom. Join our growing network of Patrons, Genetics, and Mycologist Vendors only on the 🍄 Mushroom Network!
Recommended Reads:
Beefsteak Mushroom (Fistulina Hepatica)
Welcome, fungal enthusiasts and curious minds, to an exploration of Fistulina Hepatica, commonly known as...
Read More...Magic Truffles: Psychedelic Gems of the Underground
Truffles have a hidden facet beyond their culinary uses. Certain species, often referred to as...
Read More...Caesar’s Mushroom (Amanita Caesarea)
SCIENTIFIC NAME: (Amanita Caesarea) COMMON NAME(S): Caesar’s Amanita | Royal Amanita | Orange Amanita |...
Read More...Oak Milkcap (Lactarius Quietus)
Welcome, mycology enthusiasts and nature lovers! Today, we’re journeying into the quiet corners of oak...
Read More...Whoa there, Spore Sport! 🍄 Looks like you’re not logged in yet. Don’t you know what you’re missing? MYCO-CREDITS! Imagine all the fungal fun you could have. It’s like finding a Morel in May and not picking it. Tragic, right? Log In or Become a Myco-Patron and start racking up those credits. It’s more rewarding than finding a mushroom in your backyard! 🌟🏡